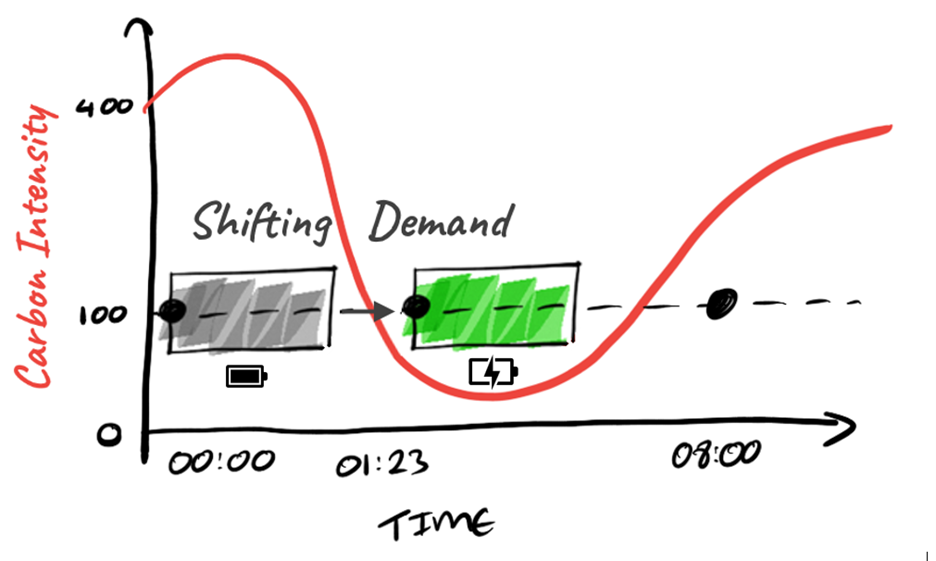
Green software is software designed and implemented to have the lowest possible carbon emissions. The Green Software Foundation (GSF) is a cross-industry consortium that is building a trusted ecosystem of people, standards, tooling and best practices for Green Software. A foundational principle of Green Software is known as carbon-aware computing, which involves shifting compute to times and places where the carbon intensity of the grid results in lower carbon emissions.
Carbon-aware computing has been at the core of the cloud partnership between two global organizations, Microsoft and UBS. This joint white paper describes their collaboration with the environmental tech nonprofit WattTime through the GSF. Together, they pioneered the first enterprise-grade carbon-aware application, and have open-sourced the tooling and architecture. To start, these organizations contributed to the development of a novel specification known as Software Carbon Intensity (SCI) that measures the carbon impact of software systems. Next, they co-developed and open-sourced the software development kit carbon-aware-sdk which allows software to run when and where energy is cleaner. The combination of both open-sourced projects empower every person and every organization on the planet to decarbonize their software.
This white paper also presents practical architectural guidance based on the minimum viable product (MVP) implementation on UBS core risk platform named Advanced Compute Quantum Analytics (ACQA). The co-developed MVP aims at reducing ACQA’s carbon impact by time-shifting compute to when the carbon intensity of the grid is lowest within a 24h window. The carbon-aware-sdk can also provide recommendations on locations with lower carbon intensity across the more than sixty global regions of Microsoft Azure’s cloud computing platform – which helps software systems to decarbonize at a global scale.
Businesses can now leverage carbon-aware computing as an innovative and viable option to reduce the carbon emissions created by their software. Organizations and software engineers are invited to contribute directly to open-source GSF projects. Please visit https://greensoftware.foundation/ for more information on the GSF, and their many initiatives to advance Green Software.
You can read and download the full whitepaper here:
 Loading...
Loading...