The ongoing impact of the COVID-19 pandemic means that, in 2020, remote working has become the new normal. And with the second wave of the virus in full swing, this doesn’t look set to change anytime soon. Even when the pandemic finally recedes, it’s likely that business leaders and employees alike will continue to prioritize ‘hybrid’ working, enacting new, more flexible ‘work from home’ policies with the option to return to the office once it is safe to do so. Recent research from Microsoft suggests this is both a challenge and an opportunity, particularly when it comes to productivity. But what are the security implications of this new world of work?
In the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic, many organizations scrambled to implement technology solutions that would ensure employees could work remotely; but security sometimes fell by the wayside in the process. As our recent Digital Defense Report highlights, this created new security vulnerabilities. For instance, most routine security tasks such as device patching or software updates needed to be done in an office environment; but in the immediate aftermath of the COVID-19 outbreak, this option temporarily disappeared. In addition, traditional security policies based on an organization controlling the perimeters of its own office network became much harder to enforce when employees were suddenly operating across home or other private networks, over which the organization had no control.
There are clear business risks associated with such vulnerabilities. But they also jeopardize employee safety and wellbeing. The pandemic has already increased pressure and stress levels for workers who had to adjust to new ways of working overnight, while also responding to the immediate impact of the crisis on their work. They don’t need to also be worrying about whether or not they are secure online while away from the confines of the office network, or that they won’t be protected enough if something goes wrong. Nor should they be overwhelmed by a multitude of security protocols, updates, and tools that hinder them from focusing on work.
So, with hybrid working here to stay, how can IT and business decision-makers support a secure, remote workforce? The answer is to deploy tools and processes that enable employees to remain focused on work, rather than having to worry about security; tools that also protect precious corporate assets and IP by default.
It’s sometimes said that a worker is only as good as their tools – and in a post-COVID remote workplace, that’s certainly true. Much of the on-premise IT infrastructure that organizations had in place before the pandemic was never designed to support remote working, and this shows. When it comes to security, more doesn’t always mean better. The patchwork of different tools and programs being used across a single organization creates frustration and reduces efficiency for workers. The goal of any security solution should be to relieve pressure from the workforce and support their mental resilience, rather than increasing stress levels with invasive or constant requests for updates and log-ins on multiple different platforms.
The use of different tools and programs also increases the likelihood of gaps – and this is where hackers can get in and information can leak out. As we settle into new ways of working for the long-haul, now is the time for IT and business leaders to take stock of and, if necessary, consolidate the existing tools and security products that they use. This also means making sure that any and all security services reflect the reality of remote working. As noted in our Digital Defense Report, this starts by taking a Zero Trust approach: i.e., treating every access attempt as if it were originating from an untrusted network. Even if employees are using VPN architecture, they may be on an insecure network – so it’s better to be safe than sorry by ensuring every access is fully authenticated, authorized, and encrypted before granting access.
But updating infrastructure isn’t enough by itself. With 73% of CISOs indicating that their organization encountered leaks of sensitive data and data spillage in the last 12 months, and with a noteworthy increase in identity-based attacks using brute force on enterprise accounts, it’s clear the human element remains a major source of concern for securing a remote workforce. CISOs and business leaders need to account for a margin of human error and put in place mechanisms that mean attack attempts can only go so far and do limited harm, even if someone in the organization does accidentally click on a phishing link or inadvertently downloads malware. This level of protection also reassures employees that they are being kept safe online, even remotely.
Strong authentication processes, such as password-less or Multi factor authentication (MFA), are the most effective means of defending against these kinds of attacks. Enabling MFA is an essential call to action for all organizations; passwords alone aren’t enough anymore. This is particularly vital for ensuring that sensitive information is protected, and that only the right people and system processes have access to sensitive information – and only when needed.
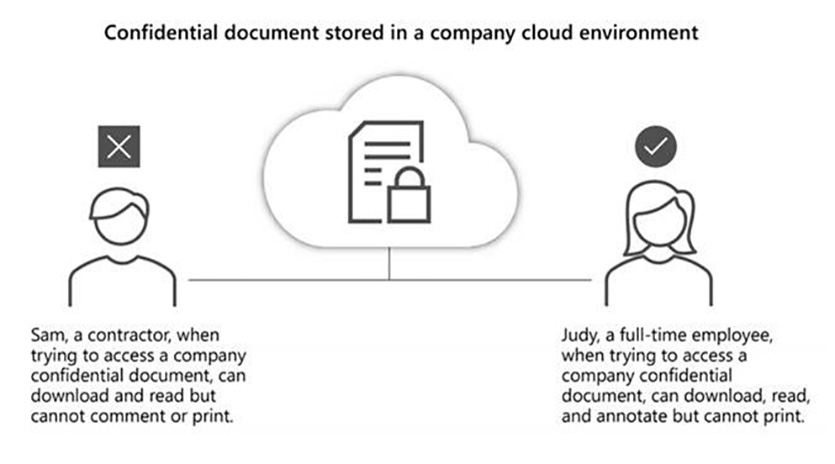
Regardless of your organization’s size or where you are on your remote work journey, the cloud can help ensure everyone stays secure, wherever they are working from. With Microsoft Azure for instance, you can manage authentication across devices, cloud apps, and on-premises apps using Active Directory, or create Conditional Access policies according to user, device, application, and risk. Meanwhile Microsoft Defender for Office 365 lets you set up antiphishing protections to help protect employees from increasingly sophisticated attacks. We also offer three authentication methods: certificate-backed virtual and physical smartcards, Windows Hello for Business (with PIN or biometric sign-in), and Azure Multi-Factor Authentication.
Most importantly, in the cloud, new security services don’t have to cost the world, since it is often a question of consolidating rather than adding features. This can generate cost savings in the long-run: with security teams able to stay ahead of threats, rather than playing catch up from afar. It also contributes to increased productivity, as employees are able to focus on their work rather than worrying about security. And finally, stronger security mechanisms reduce the risk of breaches that can end up being very costly.
Our new world of work demands a new approach to security. It’s an ongoing journey and we know that, much like adapting to remote working, it won’t happen overnight. But with the right partner, anything is possible.





