This what we are experiencing now has become a hybrid war – both a kinetic and digital. The recent and ongoing cyberattacks have been precisely targeted, with the aim to bring down Ukraine’s economy and government. Microsoft Digital Defense Report showed that the number of cyberattacks targeting critical infrastructure had grown significantly. The level of sophistication of cyberattacks permanently evolving.
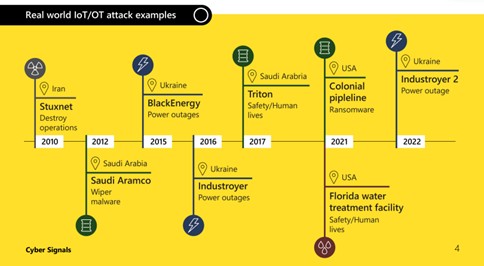
Companies now need to be extra prepared. Devices such as cameras, smart speakers, or locks and commercial appliances can become entry points for attackers, according the third edition of Cyber Signals report. This study highlighted the risks that converging IT, Internet of Things (IoT), and operational technology (OT) systems pose to critical infrastructure.
Connected Internet-of-Things* and Operational Technology (OT) devices** offer significant value to organizations looking to modernize workspaces, become more data-driven, and ease demands on staff through shifts like remote management and automation in critical infrastructure networks, if not properly secured, they increase the risk of unauthorized access to operational assets and networks Thus, over the past year, the corporation has observed threats exploiting devices in almost every part of an organization. With more than 41 billion IoT devices across enterprise and consumer environments expected by 2025 — according to International Data Corporation research — devices such as cameras, smart speakers, or locks and commercial appliances can become entry points for attackers. In Cyber Signals reported a 78% increase in disclosures of high-severity vulnerabilities from 2020 to 2022 in industrial control equipment produced by popular vendors.
Microsoft identified unpatched, high-severity vulnerabilities in 75% of the most common industrial controllers in customer Operational Technology (OT) networks.
Unlike the IT landscape of common operating systems, business applications, and platforms, OT and IoT landscapes are more fragmented, featuring proprietary protocols and devices that may not have cybersecurity standards. Attackers can have varied motives to compromise devices other than typical laptops and smartphones. For example, Russia’s cyberattacks against Ukraine, as well as other nation-state sponsored cybercriminal activity, demonstrate that some nation-state’s view cyberattacks against critical infrastructure as desirable for achieving military and economic objectives.
Establishing a more secure relationship between IT and OT require consideration of control measures. Air-gapped devices and perimeter security are no longer sufficient to address and defend against modern threats like sophisticated malware, targeted attacks, and malicious insiders, attackers also abuse of employee login credentials or exploitation of access granted to third-party suppliers and contractors to the networks.
“Throughout the entire period of the hot phase of the cyber war, which Russia started against our state on January 14, 2022, Ukrainian IT infrastructures face constant targeted cyber-attacks. That’s why we clearly understand how important complex protection of all links is: from an individual employee of the company to a third-party company that supplies software and equipment. We are only as strong as our weakest link. Government and business must join forces to prevent attacks or mitigate their consequences. Our organization with the support of leading Ukrainian and global manufacturers provides comprehensive assistance in creating solutions for cyber protection of IT infrastructures, including well secured cloud solutions, both for public and private sectors. The same time, such cooperation ensures an active exchange of best practices in the field of information protection, which is vital for joint development and the movement towards cyber resilience,” said Viktor Zhora, deputy head of the SSSCIP.
An example of a malware incident was a case of a major global food and beverage company using very old operating systems to manage factory operations. In 2022 Microsoft assisted to repel an attack while performing routine maintenance on equipment that would later connect to the Internet, malware spread to factory systems via a compromised contractor laptop. While an ICS environment can be isolated from the Internet, the moment a compromised laptop is connected to a formerly secure OT device or network it becomes vulnerable. Across the customer networks Microsoft monitors, 29% of Windows operating systems have versions that are no longer supported.
“We are facing a moment of reckoning as the world witnesses a rise in increasingly sophisticated and expansive cybersecurity attacks. Backed by unparalleled AI and human expertise Microsoft is committed to making the world a safer place for all and is the only company to deliver truly integrated end-to-end solutions across security, compliance, identity management, and privacy delivering data, insights, and predictions across our 65 trillion daily signals,” commented Leonid Polupan, the Country Manager of Microsoft Ukraine. ,,In order to support individuals and business Microsoft has broad Microsoft Security portfolio – six product families are integrating over 50 product categories.’’
Critical infrastructure security is a worldwide challenge and to face with it the – Microsoft’s Cyber Signals report recommends:
- Work with stakeholders: Map business-critical assets, in IT and OT environments.
- Device visibility: Identify what IoT and OT devices are critical assets by themselves, and which are associated with other critical assets.
- Perform a risk analysis on critical assets: Focus on the business impact of different attack scenarios as suggested by MITRE.
- Define a strategy: Address the risks identified, driving priority from business impact.
- Implement new and improved policies: Policies stemming from the Zero Trust methodology and best practices provide a holistic approach for enabling seamless security and governance across all your devices.
- Adopt a comprehensive and dedicated security solution: Enable visibility, continuous monitoring, attack surface assessment, threat detection, and response.
- Educate and train: Security teams require training specific to threats originating from or targeting IoT/OT systems.
- Examine means of augmenting existing security operations: Address IoT and OT security concerns to achieve a unified IT and OT/IoT SOC across all environments.
The attacks show that no organization is immune to the threat posed by well-funded and determined adversaries and defending against cybercriminals is a complex, ever evolving, and never-ending challenge. Protecting the internet requires policymakers, the business community, government agencies and, ultimately, individuals to make a real difference, and we can only have significant impact through shared information and partnerships.
* Operational technology (OT) – is a combination of hardware and software across programmable systems or devices that interact with the physical environment (or manage devices that interact with the physical environment).
Sources:
Reports
- Microsoft Digital Defense Report 2022
- The Convergence of IT and Operational Technology (microsoft.com)
- Evolving Zero Trust – Microsoft Position Paper
Blogs





